2. 从0到1搭建SpringCloud项目
1. 新建父工程
以“下单”需要调“支付”模块为例,从零开始搭建springcloud-001项目,陆续集成相关组件。 新建服务提供者cloud-payment工程,服务调用者cloud-order工程,完成order对payment的调用。 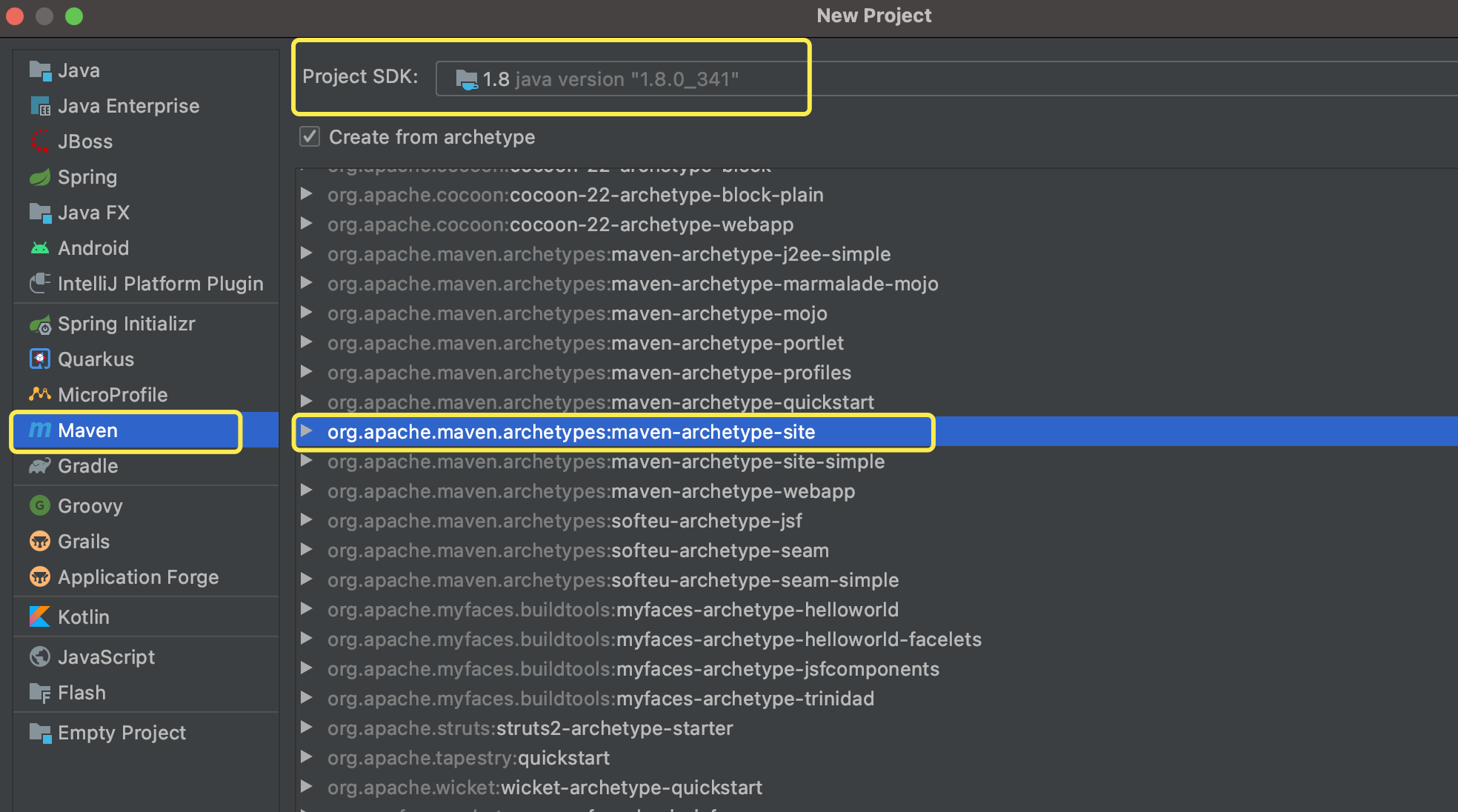
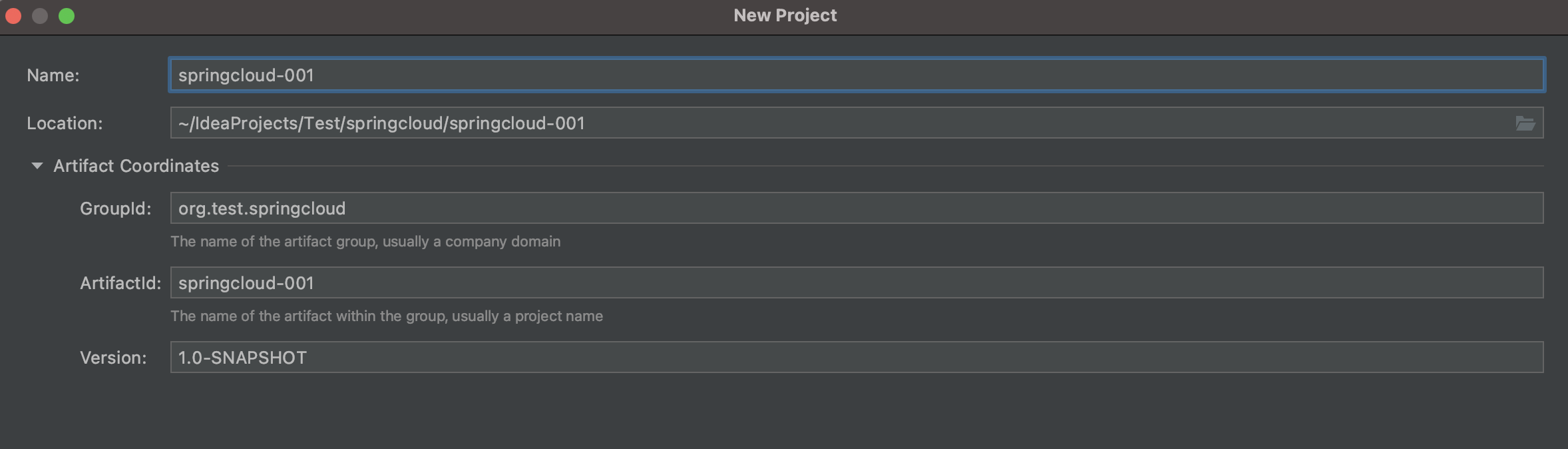
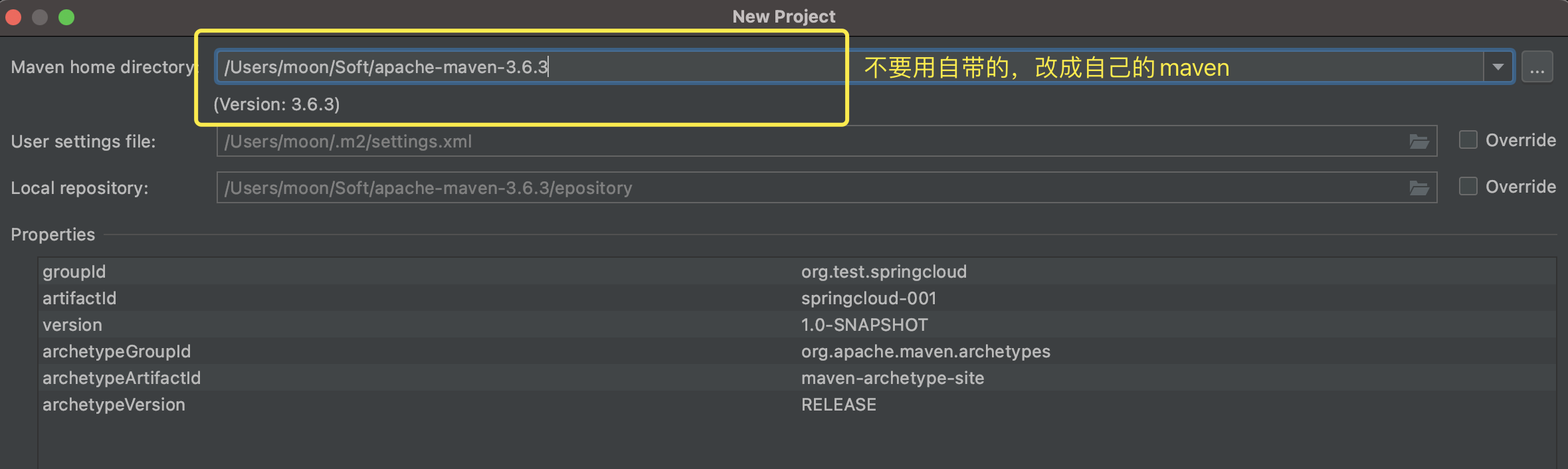
只留下pom文件,其余src等删掉。修改pom文件,添加依赖,打包方式为pom:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.test.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-001</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<!--统一管理jar包版本-->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.12</log4j.version>
<lombok.version>1.16.20</lombok.version>
<mysql.version>8.0.29</mysql.version>
<druid.verison>1.1.10</druid.verison>
<mybatisplus.version>3.1.1</mybatisplus.version>
<mybatis.spring.boot.verison>1.3.0</mybatis.spring.boot.verison>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2021.0.3</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MySql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${druid.verison}</version>
</dependency>
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis-plus -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus</artifactId>
<version>${mybatisplus.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${mybatisplus.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0.RELEASE</version>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
<addResources>true</addResources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>小回顾:
1)dependencyManagement标签和dependencies标签。dependencyManagement标签一般用在父工程,声明版本,但是不真正引入,dependencies标签一般用在子工程,真正引入依赖。只有在子项目写了该依赖,并且没有指定具体版本,才会从父项目中继承,并且version和scope都读取自父pom,如果子项目指定了版本号,那么会使用子项目指定的jar版本
2)packaging 共分为pom、jar、war类型。
- pom: 父类型都为pom类型;子模块也会用到pom,比如common通用模块。仅仅是一个引用其它maven 项目的POM。
- jar: 内部调用或者是作服务使用 packing默认类型jar类型,maven会将该项目打成jar包。
- war: 需要部署的项目。(tomcat部署)
https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/ 可以查看pom依赖
2. 建子项目-服务提供者
2.1 建module
工程右键->module->maven->选择jdk->下一步完成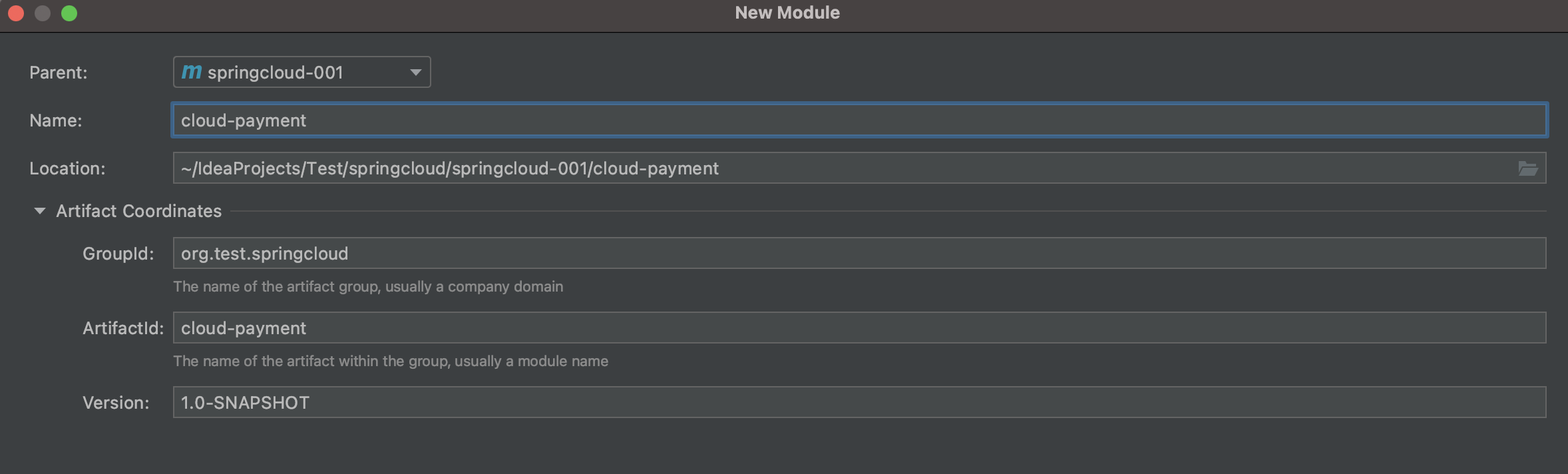
子module创建完,打开父pom,可以看到新父pom增进来modules系列标签: 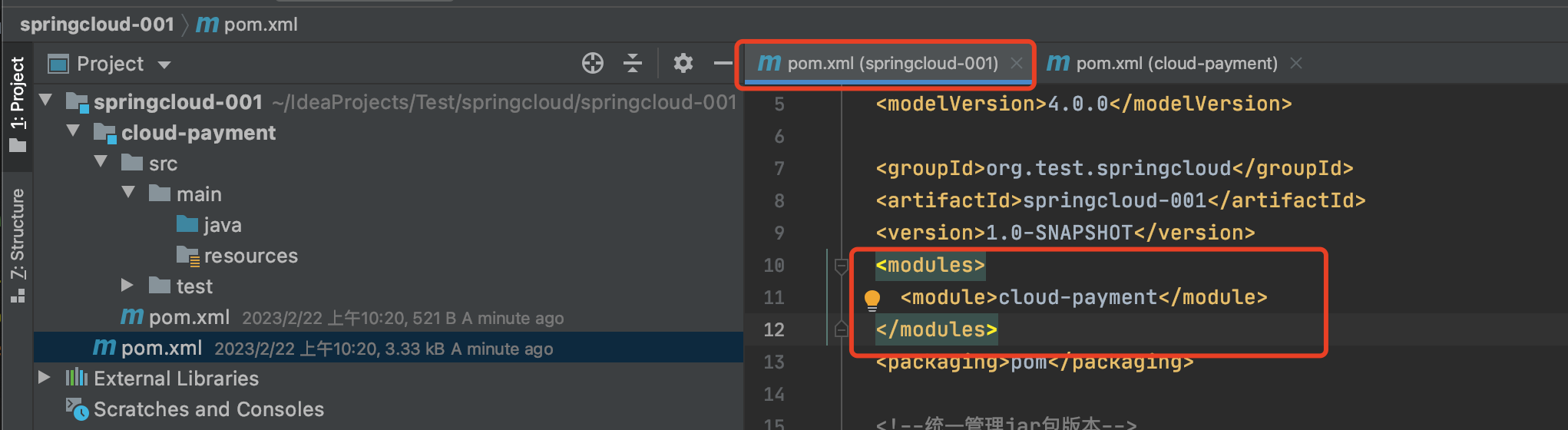 子pom中增进了parent标签:
子pom中增进了parent标签: 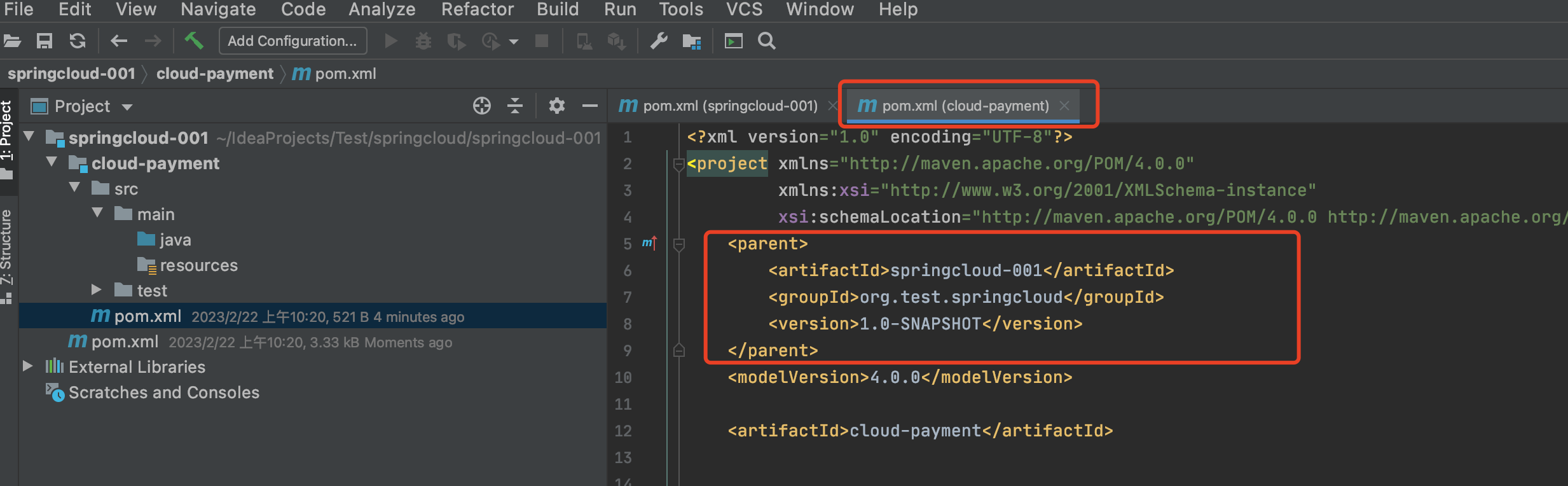
2.2 改子pom文件
继承了父工程的所以不用写version和scope,只需有 artifactId标签内容即可,添加依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud-001</artifactId>
<groupId>org.test.springcloud</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-payment</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- devtools热部署 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>2.3 写yml文件
resource->右键new file->application.yml 看到创建完的文件是个绿色树叶ok->填写配置内容:
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-payment #微服务应用的名字
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #当前数据源操作类型
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #mysql驱动包
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?allowMultiQueries=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false #useSSL安全加固
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:mapper/**/*.xml
#实体扫描,多个package用逗号或者分号分隔
typeAliasesPackage: com.test.springcloud.entitites2.4 数据库环境准备
新建库表模拟数据库环境:
CREATE TABLE `payment` (
`id` bigint unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键ID',
`serial` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '流水号',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB COMMENT='测试表';2.5 写主启动类、业务类

tip:
- 注意添加相应注解,如@service等,因为只有加入这些注解spring容器才会接管来自动装配
- 注入的类是否在application的同级包或者子孙包下面,因为2.X以后只有同级包或者子孙包才可以扫描到(1.X只有子孙包),启动类注意加上Scan相关注解
1)PaymentController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/payment")
@Slf4j
public class PaymentController {
@Resource
private PaymentService paymentService;
@PostMapping(value = "")
public CommonResult create(@RequestBody Payment payment) {
try {
paymentService.save(payment);
log.info("插入完成");
return new CommonResult(200, "插入成功", payment);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new CommonResult(500, "插入失败", null);
}
}
@GetMapping(value = "/{id}")
public CommonResult query(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
Payment payment = paymentService.getById(id);
if (payment != null) {
return new CommonResult(200, "查询成功", payment);
}
return new CommonResult(500, "查询失败", null);
}
}tip:Restful风格编写Controller:
@PostMapping增、 @DeleteMapping删、
@PutMapping改、@GetMapping查
2)PaymentService.java、PaymentServiceImpl.java、PaymentMapper.java
Mybatias-plus service层以及mapper层封装好了一些基本的增删改查方法,直接按照规范继承或实现即可,mapper里也可以少写很多。
public interface PaymentService extends IService<Payment> {
}
@Service
public class PaymentServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<PaymentMapper, Payment> implements PaymentService {
}
public interface PaymentMapper extends BaseMapper<Payment> {
}3)PaymentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.test.springcloud.dao.PaymentMapper">
<!-- 通用查询映射结果 -->
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.test.springcloud.entities.Payment">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="serial" property="serial"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 通用查询结果列 -->
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id ,serial
</sql>
</mapper>4)Payment实体类、CommonResult实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Payment implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String serial;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class CommonResult<T> {
private Integer code;
private String message;
private T data;
public CommonResult(Integer code, String message) {
this(code, message, null);
}
}2.6 测试子模块cloud-payment
测试插入POST:http://localhost:8001/payment body入参:{“serial”:“test1”} 
测试查询GET:http://localhost:8001/payment/1547406499788144642 
2.7 热部署
后期微服务增多,开启热部署,方便调试:
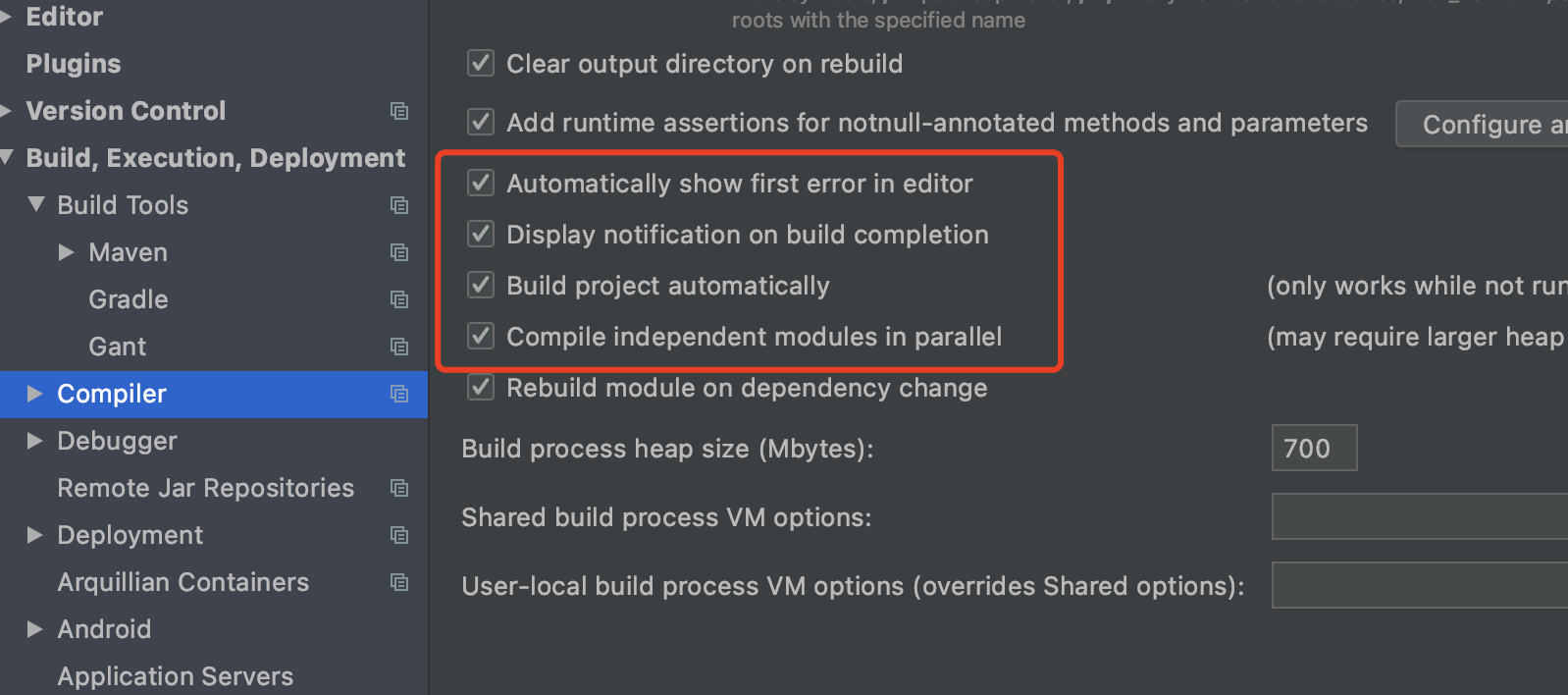
上文子pom中已经引入依赖: 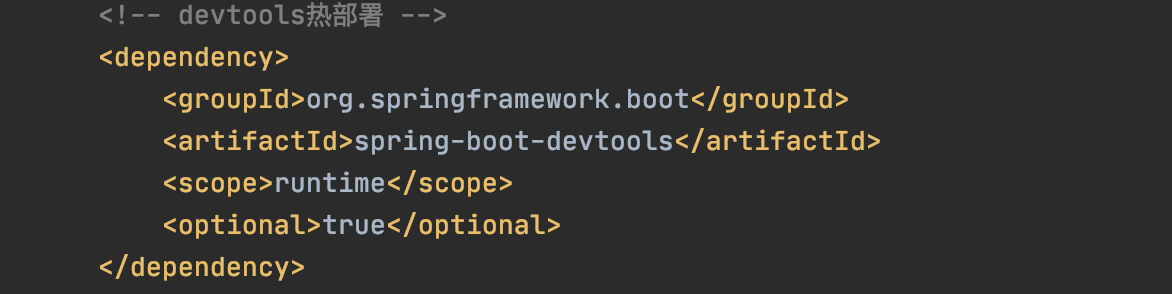
上文父pom中已经添加插件: 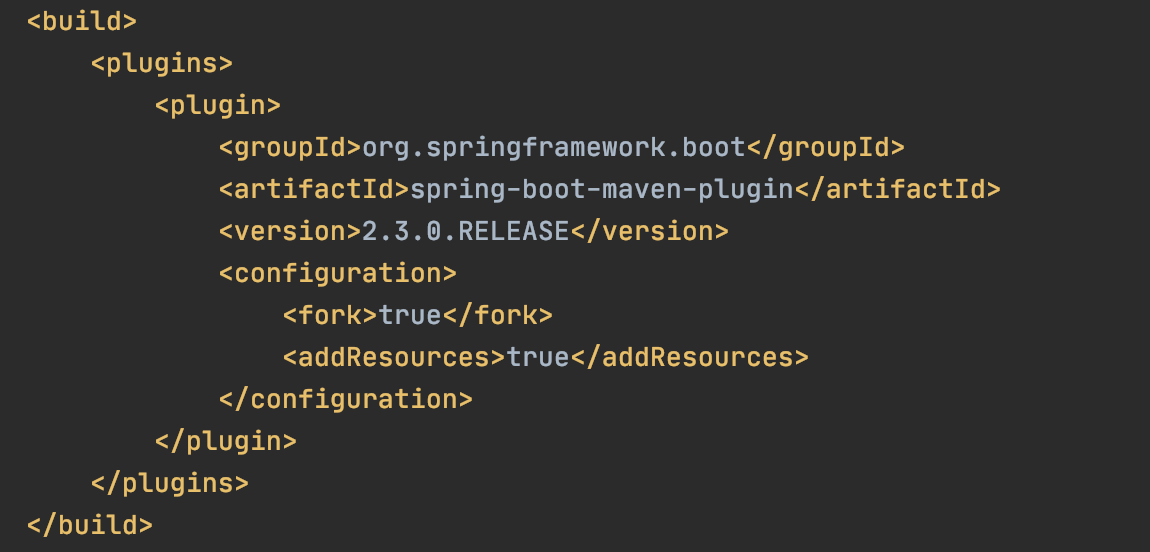
ctrl+alt+shift+/ 选择Registry->找到compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running、actionSystem.assertFocusAccessFromEdt两个勾选即可,如果没成功,重启IDEA,上线需关闭热部署。
3. 建子项目-服务消费者
同上步骤建立cloud-order工程: 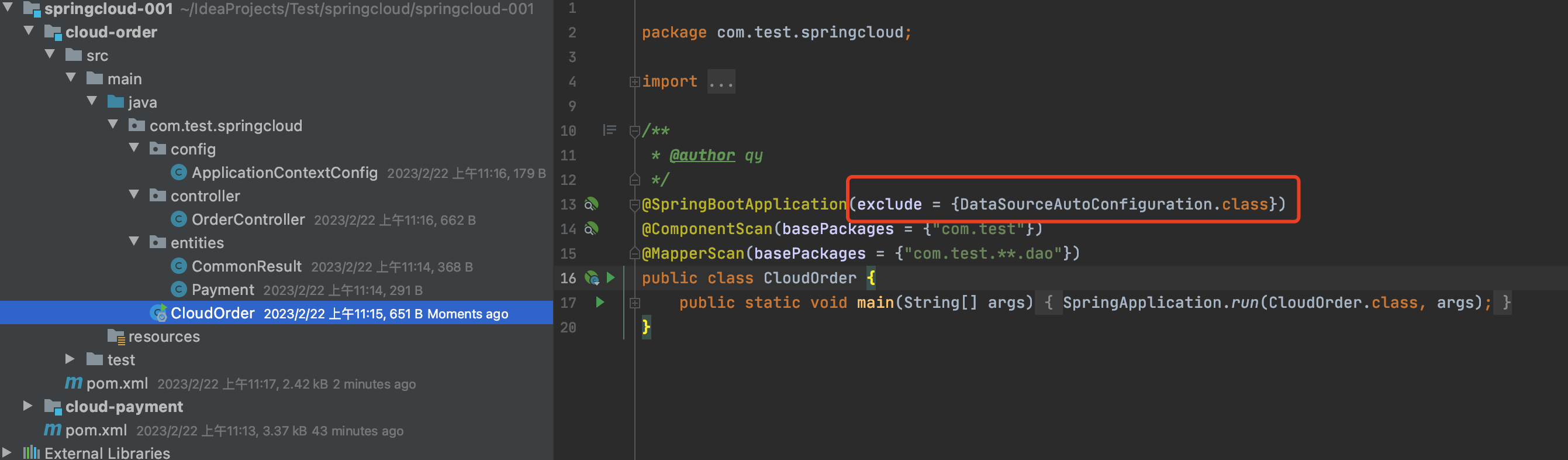
注:SpringBoot启动时会自动注入数据源,消费者工程目前不需要数据源,可通过在启动类注解上使用exclude 排除,同时将pom中数据源相关的注释掉,mybatis和mysql相关的,不然会启动报错。
OrderController .java、ApplicationContextConfig.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/consumer")
@Slf4j
public class OrderController {
public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001";
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@PostMapping("/order")
public CommonResult<Payment> createOrder(@RequestBody Payment payment) {
return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment", payment, CommonResult.class);
}
@GetMapping("/order/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getOrderPayment(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class);
}
}@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}RestTemplate:RestTemplate 是从 Spring3.0 开始支持的一个 HTTP 请求工具,它提供了常见的REST请求方案的模版,但是还是需要写一些代码,后面后讲到Feign通过注解就可以搞定。
4. 代码优化
微服务项目一般子模块会越来越多,公共的东西也就越来越多,所以一般我们抽取公共包处理: 同上新建module:cloud-common,将pom文件依赖粘贴进来,将order、payment工程中entities中相同内容剪切到common包中,将common工程maven clean->install到仓库,然后在order、payment工程中引入自定义的common包依赖:

5. 测试调用
测试插入POST:http://localhost:consumer/order 测试查询GET:http://localhost:consumer/order/1547406499788144642 不过多赘述 至此实现了order模块调用payment模块,最基础版的SpringCloud项目,后续陆续添加SpringCloud组件。