DQL语句详解
DQL
数据查询语言(Data Query Language, DQL)是SQL语言中,负责进行数据查询而不会对数据本身进行修改的语句,这是最基本的SQL语句。保留字SELECT是DQL(也是所有SQL)用得最多的动词,其他DQL常用的保留字有FROM,WHERE,GROUP BY,HAVING和ORDER BY。这些DQL保留字常与其他类型的SQL语句一起使用。
1 单表查询
查询语句的语法规则
SELECT <字段列表>
FROM <表名>
[WHERE <查询条件>]
[ORDER BY <排序字段>]
[GROUP BY <分组字段>]
# select NOW()为查询准备的表结构
CREATE TABLE t_student (
id int(3) primary key auto_increment ,
stuname varchar(30) not null ,
age int(3) ,
sex varchar(3) ,
birthday date ,
address varchar(50),
class_id int(3)
);
CREATE TABLE t_class(
class_id varchar(30) PRIMARY KEY ,
class_name varchar(30) UNIQUE ,
class_desc varchar(50)
);单表查询不带条件的查询
# 1.查询出所有的学生信息 所有的学生的所有字段的信息
select * from t_student ;
# 2.查询出所有的学生的姓名和性别
select stuname,sex from t_student;
# 3.对查询的表和列设置对应的别名
select stuname as '姓名' ,sex as "性别" from t_student;
# 别名简写可以省略 as 和 单引号
select stuname 名称 ,sex 性别 from t_student;
# 表也可以取别名
select t_student.stuname ,t_student.sex from t_student;
select t1.stuname,t1.sex from t_student as t1;
select t1.stuname,t1.sex from t_student t1;
# 自己增加查询的字段
select stuname,sex,18 常量 from t_student;
# 4.查询出所有的学生信息,并且显示的形式是【张三】18【岁】
select stuname,age,concat('【',stuname,'】',age,'【岁】') from t_student;单表查询带条件的
# 5.查询出学生表中张三的所有的信息
select * from t_student where stuname = '张三';
# 6.查询出学生表中年龄在18到22之间的学生的所有信息
select * from t_student where age >=18 and age <= 22;
select * from t_student where age BETWEEN 18 and 22 ;
# 7.查询出学生表中编号为1和3的学生信息
select *
from t_student
where id = 1 or id = 3;
select * from t_student where id in (1,3)
# 8.查询出学生表中地址信息为空的学生信息
# 不行 #
# select * from t_student where address = '';
# select * from t_student where address = null;
select * from t_student where address is null;
# 不为空的情况
select * from t_student where address is not null;
# 9.查询出所有姓张的学生的所有信息 -- 模糊查询 like
select * from t_student where stuname like '张%' ;
# 如果不加% 其实和=差不多
select * from t_student where stuname like '张三';
select * from t_student where stuname like '%三%';
# 10.查询出学生表中年龄大于20的男同学的所有信息
select * from t_student where age > 20 and sex = '男'
# 11 查询出学生表中年龄大于20或者住址在长沙的同学的所有信息
select * from t_student where age > 20 or address like '%长沙%'
# 12 查询出所有的学生信息,根据id降序 desc 降序 asc 升序【默认就是升序,也就是 asc可以省略】
select *
from t_student
order by id desc;
select *
from t_student
order by id asc;
select *
from t_student
order by id ;
# 排序我们可以根据多个字段来排列,前面的字段优先排序
# 先根据age降序排列,如果age有相同的信息,那么再根据id升序排序
select * from t_student order by age desc ,id asc;
select * from t_student order by age desc ,id desc;2 聚合函数
聚合函数一般用于统计
# 聚合函数 -- 一般用于统计
# 1.统计学员的总数 count 统计某列中非空的数据的条数
select count(*) from t_student ;
select count(id) from t_student ;
select count(address) from t_student;
select count(birthday) from t_student;
## 在实际开发中我们使用 count(1) 来统计,效率会更高
select 1,id from t_student ;
select count(1) from t_student ;
# 2.统计班级中学生最大的年龄
select max(age) from t_student ;
# 3.统计班级中学习最小的年龄
select min(age) from t_student ;
# 4.统计班级中的学员的平均年龄
select avg(age) from t_student ;
# 5.统计班级中学员的年龄总和
select sum(age) from t_student ;3 分组查询
语法规则
SELECT <字段列表>
FROM <表名>
[WHERE <查询条件>]
[ORDER BY <排序字段>]
[GROUP BY <分组字段>]
[HAVING <分组后的查询条件>]分组查询通常用于统计,一般和聚合函数配合使用
注:分组查询有一个原则,就是 select 后面的所有列中没有使用聚合函数的列,必须出现在group by后面
4 常用函数
4.1 数字函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ABS(x) | 返回x的绝对值 |
| AVG(expression) | 返回一个表达式的平均值,expression 是一个字段 |
| CEIL(x)/CEILING(x) | 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
| FLOOR(x) | 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
| EXP(x) | 返回 e 的 x 次方 |
| GREATEST(expr1, expr2, expr3, …) | 返回列表中的最大值 |
| LEAST(expr1, expr2, expr3, …) | 返回列表中的最小值 |
| LN | 返回数字的自然对数 |
| LOG(x) | 返回自然对数(以 e 为底的对数) |
| MAX(expression) | 返回字段 expression 中的最大值 |
| MIN(expression) | 返回字段 expression 中的最大值 |
| POW(x,y)/POWER(x,y) | 返回 x 的 y 次方 |
| RAND() | 返回 0 到 1 的随机数 |
| ROUND(x) | 返回离 x 最近的整数 |
| SIGN(x) | 返回 x 的符号,x 是负数、0、正数分别返回 -1、0 和 1 |
| SQRT(x) | 返回x的平方根 |
| SUM(expression) | 返回指定字段的总和 |
| TRUNCATE(x,y) | 返回数值 x 保留到小数点后 y 位的值(与 ROUND 最大的区别是不会进行四舍五入) |
案例
# 数字函数
# abs函数 取绝对值
select abs(-100) ;
# avg() 取平均值
select avg(age) from t_student;
# CEIL(x)/CEILING(x)
select ceil(2.5) ;
select ceil(avg(age) ) from t_student;
select ceiling(3) ;
select ceil(3) ;
# floor
select floor(2.5) ;
# exp e的3次方
select exp(3) ;
# GREATEST(expr1, expr2, expr3, …) 返回列表中的最大值
select GREATEST(1,4,5,3,9,2) ;
# LEAST(value1,value2,...) 返回列表中的最小值
select LEAST(1,4,5,3,9,2) ;
# LN 自然对数
select ln(2) ;
# LOG(x)
select log(20) ;
# POW(x,y) 返回x的y次方
select POW(2,3) ;
# RAND() 返回0~1的随机值
select RAND() ;
# ROUND(x) 返回离x最近的整数
select round(5.12) ;
# SIGN(x) 判断x的符号 大于0 等于0 小于0 1 0 -1
select sign(99),sign(0),sign(-199);
# SQRT(x) x的平方根
select SQRT(9);
# TRUNCATE(x,y)
select TRUNCATE(3.15926,3),TRUNCATE(3.15926,2) ;4.2 字符串函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ASCII(s) | 返回字符串 s 的第一个字符的 ASCII 码 |
| LENGTH/CHAR_LENGTH(s)/CHARACTER_LENGTH(s) | 返回字符串 s 的字符数 |
| CONCAT(s1,s2…sn) | 字符串 s1,s2 等多个字符串合并为一个字符串 |
| FIND_IN_SET(s1,s2) | 返回在字符串s2中与s1匹配的字符串的位置 |
| FORMAT(x,n) | 函数可以将数字 x 进行格式化 “#,###.##”, 将 x 保留到小数点后 n 位,最后一位四舍五入 |
| INSERT(s1,x,len,s2) | 字符串 s2 替换 s1 的 x 位置开始长度为 len 的字符串 |
| LOCATE(s1,s) | 从字符串 s 中获取 s1 的开始位置 |
| LCASE(s)/LOWER(s) | 将字符串 s 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
| UCASE(s)/UPPER(s) | 将字符串 s 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
| TRIM(s) | 去掉字符串 s 开始和结尾处的空格 |
| LTRIM(s) | 去掉字符串 s 开始处的空格 |
| RTRIM(s) | 去掉字符串 s 结尾处的空格 |
| SUBSTR(s, start, length) | 从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串 |
| SUBSTR/SUBSTRING(s, start, length) | 从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串 |
| POSITION(s1 IN s) | 从字符串 s 中获取 s1 的开始位置 |
| REPEAT(s,n) | 将字符串 s 重复 n 次 |
| REVERSE(s) | 将字符串s的顺序反过来 |
| STRCMP(s1,s2) | 比较字符串 s1 和 s2,如果 s1 与 s2 相等返回 0 ,如果 s1>s2 返回 1,如果 s1<s2 返回 -1 |
# 字符串函数
# ASCII 查看第一个字符的ASCII值
select ascii('ABC'),ascii('BC');
# length 返回字符串的长度 字符个数
select length('abcd1234'),CHAR_LENGTH('abcd1234');
# CONCAT(s1,s2…sn) 字符串拼接
select id,stuname ,age,concat('【',id,'】',stuname) from t_student
# FIND_IN_SET(s1,s2) 返回在字符串s2中与s1匹配的字符串的位置
select FIND_IN_SET("c","a,b,c,d,e,f,g");
select FIND_IN_SET('c','a,b,c,d,e,f,g');
# FORMAT(x,n) 函数可以将数字 x 进行格式化 “#,###.##”, 将 x 保留到小数点后 n 位,最后一位四舍五入
select FORMAT(19999999999.5678,2);
# INSERT(s1,x,len,s2) 字符串 s2 替换 s1 的 x 位置开始长度为 len 的字符串
select INSERT("www.baidu.com",5,5,"sinax") ;
# LOCATE(s1,s) 从字符串 s 中获取 s1 的开始位置
select LOCATE("a","bcdaefg");
# LCASE(s)/LOWER(s) 转换为小写
# UCASE(s)/UPPER(s) 转换为大写
select lcase('ABCedfgDDDddd'),LOWER('ABCedfgDDDddd'),UCASE('ABCedfgDDDddd'),UPPER('ABCedfgDDDddd') ;
# TRIM(s) 去掉字符串 s 开始和结尾处的空格
# LTRIM(s) 去掉字符串 s 开始空格
# RTRIM(s) 去掉字符串 s 结尾处的空格
select TRIM(' abc def '),LTRIM(' abc def '),RTRIM(' abc def ');
# SUBSTR(s, start, length) SUBSTRING 从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串
select substr("abcdefg1234566",4,5) ;
# POSITION(s1 IN s) 从字符串 s 中获取 s1 的开始位置
select POSITION("123" in "abcdefg1235")
# REPEAT(s,n) 将字符串 s 重复 n 次
select REPEAT("hello-",5);
# REVERSE(s) 将字符串s的顺序反过来
select REVERSE("abcdefg") ;
# STRCMP(s1,s2) 比较字符串 s1 和 s2,如果 s1 与 s2 相等返回 0 ,如果 s1>s2 返回 1,如果 s1<s2 返回 -1
select STRCMP("abc","abc") ,STRCMP("a1","a2"),STRCMP("a2","a1") ;4.3 日期函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| CURDATE()/CURRENT_DATE() | 返回当前日期 |
| CURRENT_TIME()/CURTIME() | 返回当前时间 |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() | 返回当前日期和时间 |
| ADDDATE(d,n) | 计算起始日期 d 加上 n 天的日期 |
| ADDTIME(t,n) | 时间 t 加上 n 秒的时间 |
| DATE() | 从日期或日期时间表达式中提取日期值 |
| DAY(d) | 返回日期值 d 的日期部分 |
| DATEDIFF(d1,d2) | 计算日期 d1->d2 之间相隔的天数 |
| DATE_FORMAT(f) | 按表达式 f的要求显示日期 d |
| DAYNAME(d) | 返回日期 d 是星期几,如 Monday,Tuesday |
| DAYOFMONTH(d) | 计算日期 d 是本月的第几天 |
| DAYOFWEEK(d) | 日期 d 今天是星期几,1 星期日,2 星期一,以此类推 |
| EXTRACT(type FROM d) | 从日期 d 中获取指定的值,type 指定返回的值 type可取值为: MICROSECOND SECOND MINUTE HOUR DAY WEEK MONTH QUARTER YEAR SECOND_MICROSECOND MINUTE_MICROSECOND MINUTE_SECOND HOUR_MICROSECOND HOUR_SECOND HOUR_MINUTE DAY_MICROSECOND DAY_SECOND DAY_MINUTE DAY_HOUR YEAR_MONTH |
| DAYOFWEEK(d) | 日期 d 今天是星期几,1 星期日,2 星期一,以此类推 |
| UNIX_TIMESTAMP() | 得到时间戳 |
| FROM_UNIXTIME() | 时间戳转日期 |
# 日期时间函数
select now();
# CURDATE()/CURRENT_DATE() 返回当前日期
select CURDATE(),CURRENT_DATE() ;
# CURRENT_TIME()/CURTIME() 返回当前时间
select CURTIME() , CURRENT_TIME() ;
# now() CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() 返回当前日期和时间
select now(),CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() ;
# ADDDATE(d,n) 计算起始日期 d 加上 n 天的日期
select ADDDATE("2022-01-26",6) ,ADDDATE(now(),10) ;
# ADDTIME(t,n) 时间 t 加上 n 秒的时间
select ADDTIME('2022-01-02 11:11:11',59),ADDTIME(now(),60*60)
# DATE() 从日期或日期时间表达式中提取日期值
select date('2022-01-02 11:11:11') ,date(now());
# DAY(d) 返回日期值 d 的日期部分
select day('2022-01-02 11:11:11'),day(now()) ;
# DATEDIFF(d1,d2) 计算日期 d1->d2 之间相隔的天数
select DATEDIFF("2021-12-23","2022-01-01") ,DATEDIFF("2022-01-01","2021-12-23");
# DATE_FORMAT(f) 按表达式 f的要求显示日期 d
select DATE_FORMAT(now(),"%Y-%m-%d %r") ,DATE_FORMAT(now(),"%Y-%m-%d %H:%I:%S");
# DAYNAME(d) 返回日期 d 是星期几,如 Monday,Tuesday
select DAYNAME(now()),DAYNAME("2022-02-14")
# DAYOFMONTH(d) 计算日期 d 是本月的第几天
select DAYOFMONTH(now()),DAYOFMONTH("2022-02-14");
# DAYOFWEEK(d) 日期 d 今天是星期几,1 星期日,2 星期一,以此类推
select DAYOFWEEK(now()) ,DAYOFWEEK("2022-02-14");
# EXTRACT(type FROM d) 从日期 d 中获取指定的值,type 指定返回的值
select EXTRACT(DAY from now())
,EXTRACT(WEEK from now())
,EXTRACT(HOUR from now())
,EXTRACT(SECOND from now())
,EXTRACT(MINUTE from now())
# UNIX_TIMESTAMP() 获取时间戳
select UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2022-01-01')
# FROM_UNIXTIME() 根据时间戳转换为日志
select FROM_UNIXTIME(1640966400) ;4.4 高级函数
CASE函数,类似于Java中Switch语句
语法:
CASE WHEN condition1 THEN result1 WHEN condition2 THEN result2 WHEN conditionN THEN resultN ELSE result END;
# 高级函数
# case函数
select * from t_student ;
select
id,stuname,age
,case
when age < 18 then '[0-18]'
when age BETWEEN 18 and 20 then '[18-20]'
when age BETWEEN 20 and 30 then '[20-30]'
else '[30以上]'
end
from t_student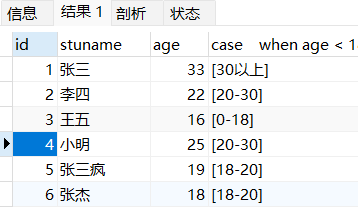
IF函数
IF()函数在条件为TRUE时返回一个值,如果条件为FALSE则返回另一个值。
语法:IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)
# IF语句
select
t.* ,if(age >=18,'成年人','青少年'),if(sex='男',1,0)
from t_student t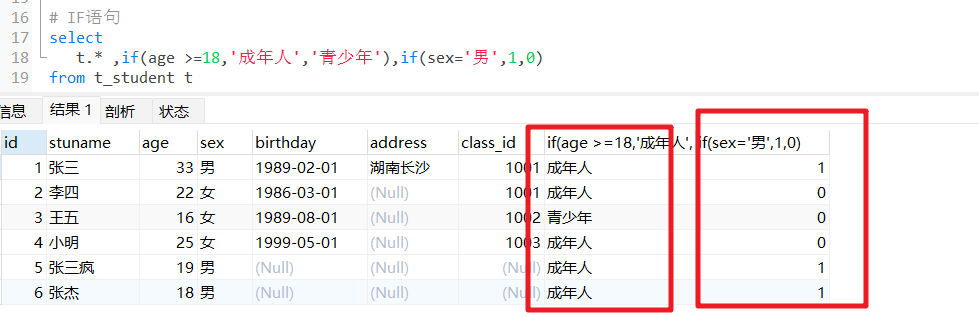
IFNULL函数
如果表达式为NULL,则IFNULL()函数返回指定的值。如果表达式为NOT NULL,则此函数返回表达式。
语法:IFNULL(expression, alt_value)
# IFNULL 函数
select t.* ,ifnull(address,"中国") from t_student t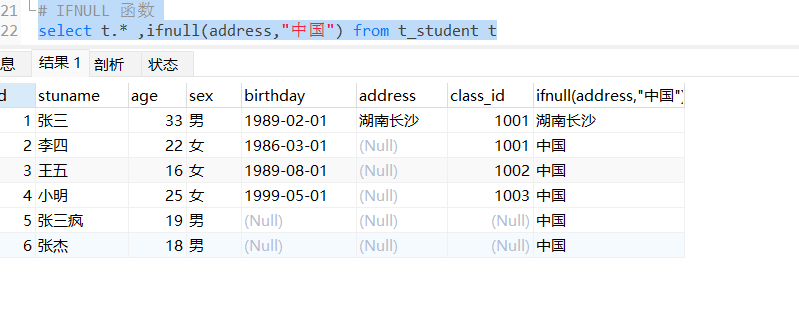
ISNULL函数
ISNULL()函数返回1或0,具体取决于表达式是否为NULL。如果expression为NULL,则此函数返回1.否则,返回0。
语法:ISNULL(expression)
# ISNULL() 函数
select t.* ,ISNULL(address) from t_student t;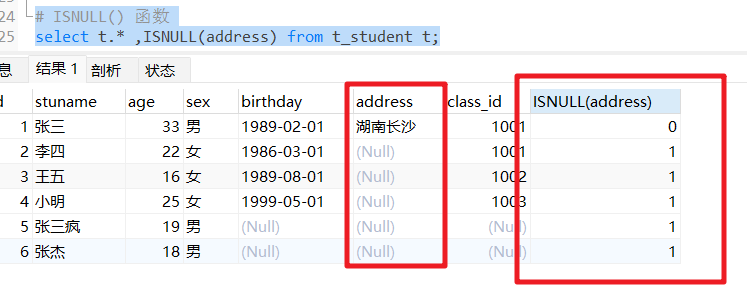
NULLIF函数
NULLIF()函数比较两个表达式,如果它们相等则返回NULL。 否则,返回第一个表达式。
语法:NULLIF(expr1, expr2)
# NULLIF函数 如果两个表达式相同就返回null,否则返回第一个表达式
select NULLIF('a','b'),NULLIF('a1','a1') ;
CAST函数
CAST()函数将(任何类型的)值转换为指定的数据类型。
语法:CAST(value AS datatype)
# CAST函数
select CAST('2022-02-13' as DATE) ;
select CAST('2022-02-13 12:12:24' as TIME) ;
select CAST(97 as CHAR) ;
select CAST(5-20 as SIGNED) ;
select CAST(12.666 as DECIMAL);
select CAST('66' as BINARY);5 多表查询
5.1 交叉连接
交叉连接是不带WHERE 子句的多表查询,它返回被连接的两个表所有数据行的笛卡尔积
SELECT *
FROM T_A , T_B案例
# 交叉连接
select t1.* ,t2.*
from t_student t1,t_class t2;
5.2 内连接
在交叉连接的基础上增加连接的条件,不需要连接无效的记录
SELECT *
FROM T_A INNER JOIN T_B ON T_A.SID = T_B.SID
# 等价于
SELECT *
FROM T_A,T_B
WHERE T_A.SID = T_B.SID案例
# 内连接 : 在交叉连接的基础上增加连接的条件,不需要连接无效的记录
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_student t1 INNER JOIN t_class t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id # on 关键字后面的是连接的条件
5.3 外连接
左连接
select t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 left outer join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.id右连接
select t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 right join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.id全连接
select t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 full join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.id案例
# 外连接: 找到学生表中的所有的学生信息及对应的班级信息
# 内连接只会保留满足连接条件的记录
# 左外连接: 在内连接的基础上保留了左侧表结构中不满足连接条件的记录
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_student t1 LEFT JOIN t_class t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id
# 右外连接:在内连接的基础上保留了右侧表结构中不满足连接条件的记录
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_Class t1 RIGHT JOIN t_student t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_class t1 LEFT JOIN t_student t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id
# 全连接
# 全连接的作用是 在内连接的基础上保留的左右两边不满足条件的记录,但是在MySQL中已经移除了全连接,但是在Oracle或者其他的数据库中是存在的。
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_student t1 LEFT JOIN t_class t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id;
# 对应的全连接操作
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_student t1 FULL JOIN t_class t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id;
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_class t1 LEFT JOIN t_student t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id;
select t1.*,t2.*
from t_class t1 FULL JOIN t_student t2
on t1.class_id = t2.class_id;等价于 : union 与union all区别
select t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 left outer join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.id
union
select t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 right join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.idselect t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 left outer join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.id
union all
select t1.*, t2.* from t_student t1 right join t_class t2 on t1.classid=t2.idunion和union all都能实现结果集的合并
union合并结果集后会取出重复的记录

union all 合并结果集后不会移除重复的记录

5.4 子查询
# 子查询 嵌套查询
# 查询出班级为 java1班 的所有的学员信息
select t1.*
from t_student t1
where class_id in (
select t_class.class_id from t_class where t_class.class_name = 'java1班' or t_class.class_name = 'java2班'
)
# 如果在子查询中只有一条记录那么我们可以用=来替代in
select t1.*
from t_student t1
where class_id = (
select t_class.class_id from t_class where t_class.class_name = 'java1班' or t_class.class_name = 'java2班'
)
select t1.*
from t_student t1
where EXISTS # exists 存在于的含义 外表中的记录存在于子表中 就满足条件 否则就过滤掉
(
select t_class.class_id from t_class where t_class.class_name = 'java1班' and t1.class_id = t_class.class_id
)6 综合案例
drop table student;
create table student (
id int(3) PRIMARY KEY ,
name varchar(20) not null,
sex varchar(4),
birth int(4),
department varchar(20),
address varchar(50));
# 创建score表。SQL代码如下:
drop table score;
create table score(
id int(3) PRIMARY KEY ,
stu_id int(3) not null,
c_name varchar(20) ,
grade int(3)
)
-- 向student表插入记录的INSERT语句如下:
insert into student values(901,'张老大','男',1985,'计算机系','北京市海淀区');
insert into student values(902,'张老二','男',1986,'中文系','北京市昌平区');
insert into student values(903,'张三','女',1990,'中文系','湖南省永州市');
insert into student values(904,'李四','男',1990,'英语系','辽宁省阜新市');
insert into student values(905,'王五','女',1991,'英语系','福建省厦门市');
insert into student values(906,'王六','男',1988,'计算机系','湖南省衡阳市');
-- 向score表插入记录的INSERT语句如下:
insert into score values(1,901,'计算机',98);
insert into score values(2,901,'英语',80);
insert into score values(3,902,'计算机',65);
insert into score values(4,902,'中文',88);
insert into score values(5,903,'中文',95);
insert into score values(6,904,'计算机',70);
insert into score values(7,904,'英语',92);
insert into score values(8,905,'英语',94);
insert into score values(9,906,'计算机',90);
insert into score values(10,906,'英语',85);
SELECT * from student;
select * from score;
1、查询student表的第2条到4条记录
select * from student LIMIT 1,3;
2、从student表查询所有学生的学号(id)、
姓名(name)和院系(department)的信息
select id '学号' ,name as '姓名' ,department 院系
from student t
3、从student表中查询计算机系和英语系的学生的信息
select *
from student t
where t.department = '计算机系' or t.department='英语系'
select *
from student t
where t.department in ('计算机系','英语系')
4、从student表中查询年龄25~30岁的学生信息
select *,EXTRACT(year from now()) ,EXTRACT(year from now())-birth age
from student where (EXTRACT(year from now()) - birth) BETWEEN 30 and 40;
5、从student表中查询每个院系有多少人
select t.department,count(1)
from student t
group by t.department
6、从score表中查询每个科目的最高分
select s.c_name,max(grade)
from score s
group by s.c_name
7、查询李四的考试科目(c_name)和考试成绩(grade)
注意: '=' 只有在确定结果是一个的情况下使用,不确定的使用用 'in'
select c_name,grade
from score
where stu_id in (
select id from student where name = '李四'
)
# 通过exists
select c_name ,grade
from score s
where EXISTS (
select id from student where name = '李四' and student.id = s.stu_id
)
# 通过左连接来实现
select t1.*
from score t1 RIGHT join ( select * from student where name = '李四') t2
on t1.stu_id = t2.id ;
select t1.*,t2.*
from score t1 RIGHT join student t2
on t1.stu_id = t2.id
where t2.name = '李四'
8、用内连接的方式查询所有学生的信息和考试信息
select t1.*,t2.*
from student t1 INNER JOIN score t2
on t1.id = t2.stu_id
9、计算每个学生的总成绩
select stu_id,sum(grade)
from score
group by stu_id
select stu_id,(select name from student where id = stu_id) 姓名,sum(grade)
from score
group by stu_id
select t1.name,sum(t2.grade)
from student t1 INNER JOIN score t2
on t1.id = t2.stu_id
group by t1.name
10、计算每个考试科目的平均成绩
select c_name,TRUNCATE(avg(grade),2) 平均分
from score
group by c_name
11、查询计算机成绩低于95的学生信息
select *
from student
where id in (
select stu_id from score where c_name = '计算机' and grade < 95
)
select *
from student
where EXISTS (
select stu_id from score where c_name = '计算机' and grade < 95 and student.id = stu_id
)
12、查询同时参加计算机和英语考试的学生的信息
select * from score;
# 首先查询出 参加计算机的学员
select * from score where c_name = '计算机'
select * from score where c_name = '英语'
select * from student where id in (
select stu_id from score where stu_id in (
select stu_id from score where c_name = '计算机' )
and c_name = '英语' )
13、将计算机考试成绩按从高到低进行排序
select *
from score
where c_name = '计算机'
order by grade desc
14、从student表和score表中查询出学生的学号,
然后合并查询结果 UNION与union all
select id
from student
union
select stu_id
from score
select id
from student
union all
select stu_id
from score
15、查询姓张或者姓王的同学的姓名、院系和考试科目及成绩
select name 姓名, department 院系, c_name 考试科目 ,grade 成绩
from student t1 left join score t2 on t1.id = t2.stu_id
where t1.name like '张%' or t1.name like '王%'
select name 姓名, department 院系, c_name 考试科目 ,grade 成绩
from (select * from student where name like '张%' or name like '王%') t1 left join score t2 on t1.id = t2.stu_id
16、查询都是湖南的学生的姓名、年龄、院系和考试科目及成绩
select name 姓名, (EXTRACT(year from now()) - birth) 年龄, department 院系, c_name 考试科目 ,grade 成绩
from student t1 left join score t2
on t1.id = t2.stu_id
where address like '湖南%'